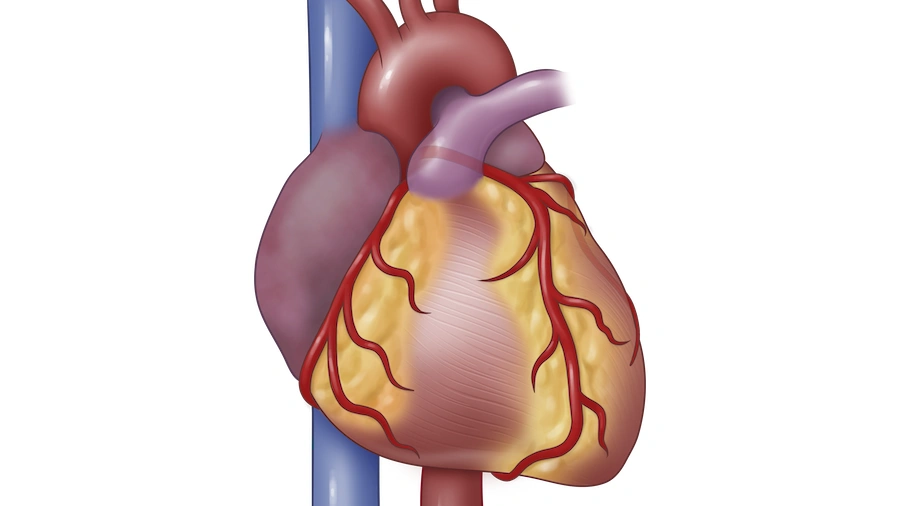
Heart Attack
Heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, resulting in damage to the heart muscle. Every 40 seconds someone in the United States has a heart attack. Of the approximately 805,000 Americans who experience a heart attack each year, about 605,000 people experience a first attack.
More About This Condition
A heart attack occurs when blood flow that carries oxygen to the heart is blocked. This can happen due to a buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which are responsible for delivering oxygen and nutrients to the heart. If blood flow is blocked for an extended period, the heart muscle can become damaged or die.
IMPORTANT NOTE: This overview is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for talking with your doctor. Be sure to talk with your doctor for a complete discussion of this condition as well as the benefits and risks of any treatment options.
The symptoms of a heart attack can vary from person to person, and some individuals may experience no symptoms at all. However, it is important to be aware of the following warning signs, which may indicate a heart attack:
- Chest pain, heaviness, or discomfort in the center or left side of the chest
- Pain or discomfort in one or both arms, your back, shoulders, neck, jaw, or above your belly button
- Shortness of breath when resting or doing a little bit of physical activity
- Sweating a lot for no reason
- Feeling unusually tired, sometimes for days
- Nausea (feeling sick to the stomach) and vomiting
- Light-headedness or sudden dizziness
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately. Quick treatment can reduce the amount of damage to the heart muscle and improve your chances of recovery.
Your doctor may:
- Ask you or a family member about your medical history.
- Conduct a physical examination.
Your doctor may order one of more of the following tests:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG) is the most common initial test and may be given within minutes of your arrival at the hospital.
- Blood tests can measure levels of specific proteins released by heart muscle cells during a heart attack.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan is an imaging test that uses a combination of X-rays and computer technology to produce images of the body. CT with contrast, a dye-like substance, enhances the image of the organ or tissue under study.
- Stress tests usually involve physical exercise such as walking on a treadmill or riding a stationary bicycle.
Treatment
Treatment for this condition must always be discussed with your doctor for a full discussion of options, risks, benefits, and other information.
The treatment for a heart attack typically involves restoring blood flow to the heart as quickly as possible. This may involve the following:
- Medications, such as aspirin, nitroglycerin, or thrombolytic therapy, can help dissolve blood clots and reduce the workload on the heart.
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), also called coronary angioplasty, is a nonsurgical procedure that improves blood flow to your heart.
- Stenting involves the placement of a small wire mesh tube in a narrowed or blocked artery to help keep it open.
- Coronary artery bypass surgery is a procedure in which a healthy blood vessel is taken from another part of the body and used to bypass a blocked artery.
- Mechanical thrombectomy is a minimally invasive procedure that physically removes clot from blocked blood vessels.
