Neuro Arteriovenous Malformation
Neuro Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a rare condition that affects less than 1% of the population. In most cases, AVMs do not cause symptoms and are only discovered by chance in the treatment of unrelated conditions. Nonetheless, early diagnosis and treatment are crucial because AVMs can lead to serious health complications, including stroke.
More About This Condition
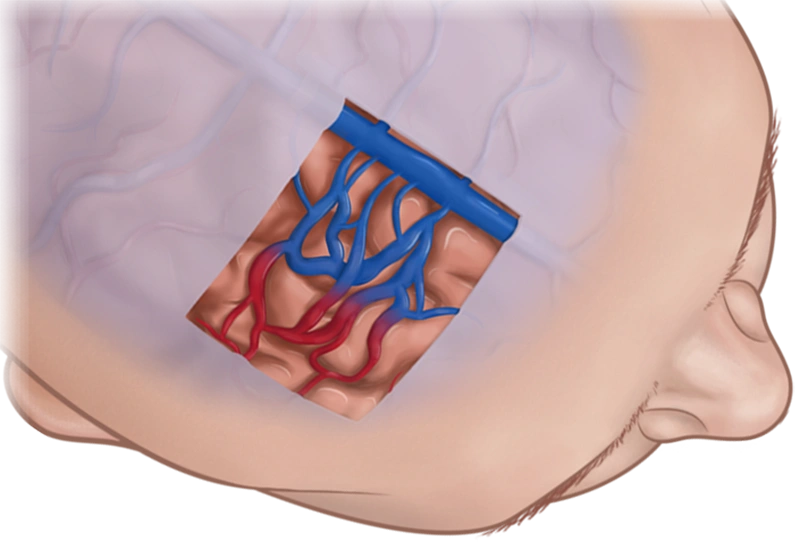
AVMs are malformed blood vessels that cause direct and irregular connections between arteries and veins due to an absence of capillaries—a network of small blood vessels that delivers oxygen to cells. In most cases, AVMs cause damage by reducing the amount of oxygen reaching brain tissue and by compressing or displacing parts of the brain. Over time, increased blood flow through arteries directly into veins can cause some AVMs to grow progressively larger, weaken, and rupture, causing hemorrhagic stroke.
A hemorrhagic stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when blood from damaged or ruptured blood vessels seeps into or around the brain. Intracranial bleeding disrupts the brain’s oxygen supply and upsets the chemical balance that brain cells need to function. The resulting blood clot (hematoma) can cause the brain to swell (edema) and increase intracranial pressure, which can cause further oxygen deprivation.
IMPORTANT NOTE: This overview is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for talking with your doctor. Be sure to talk with your doctor for a complete discussion of this condition as well as the benefits and risks of any treatment options.
People with AVMs experience few, if any, significant symptoms. If symptoms are present, they typically include:
- headache
- weakness
- seizures
- pain
- dizziness
- problems with speech, vision, or movement
- loss of consciousness
- memory deficits
Diagnosis
Your doctor may:
- Conduct a physical examination.
- Ask about signs and symptoms.
Your doctor may order one or more of the following imaging tests:
- Cerebral angiography, also called cerebral arteriography, provides the most accurate pictures of blood vessel structure. A special water-soluble dye, called a contrast agent, is injected into an artery so that blood vessels can be more easily seen on X-rays.
- Computed tomography (CT scan) uses X-rays to create an image of the head, brain, or spinal cord and are especially useful in revealing the presence of hemorrhage.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) can record the pattern and speed of blood flow through vascular lesions as well as the flow of cerebrospinal fluid throughout the brain and spinal cord.
- Transcranial Doppler ultrasound can detect medium and large AVMs, as well as the presence and amount of hemorrhage. It evaluates blood flow through the brain by directing high-frequency sound waves through the skull at specific arteries. Sound wave signals that bounce back from blood cells are interpreted by a computer to create an image of the velocity of blood flow.
Treatment
Treatment for this condition must always be discussed with your doctor for a full discussion of options, risks, benefits, and other information.
Medication can relieve general AVM symptoms.
Endovascular embolization, a minimally invasive treatment that blocks blood flow to problem areas, may be the appropriate treatment in some cases. To reach an AVM, a catheter (tube) is inserted through an incision in the femoral artery at the groin and threaded towards the brain. Your doctor will use fluoroscopy (a type of X-ray) to track the catheter through the arteries, up to the affected site. Once in position, a substance (such as balloons, coils or a fast-drying, glue-like material) is pushed through the tube and released into the enlarged space.
